Indroduction
One of the most revolutionary inventions in contemporary history is the blockchain revolution. Fundamentally, blockchain technology is changing our understanding of transparency, trust, and value exchange in the digital sphere. By providing a new paradigm where data integrity, security, and trust are built into the technology itself, blockchain, a decentralized, distributed ledger, removes the need for middlemen. This fundamental change has broad ramifications, affecting everything from government and healthcare to supply chains and finance.

This essay will examine how it is changing the definition of trust and transparency in the digital era, how it affects different industries, and the opportunities and difficulties it poses for creating a future that is more safe, decentralized, and egalitarian.
What is Blockchain Technology?
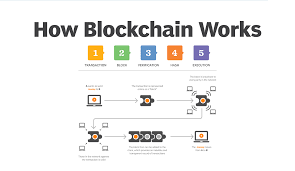
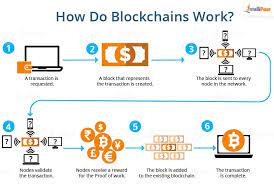
A distributed ledger technology (DLT) called it makes it possible to record data or transactions across a network of computers in a safe, transparent, and impenetrable manner. A list of transactions is contained in each block of the chain, which is connected in chronological order to form an unchangeable chain of data. Due to its decentralized nature, which eliminates a single point of failure or control, blockchain technology is extremely resistant to fraud and hacking.
The following are some of the main characteristics of blockchain that help it redefine transparency and trust:
- Decentralization: It eliminates the need for a middleman or central authority. Rather, a network of participants shares control, guaranteeing that no one party has the authority to alter or control the data.
- Transparency: The same data is accessible to all members of a blockchain network. Transactions cannot be removed or changed once they are recorded, allowing for the tracing of all previous chain interactions.
- Immutability: Data on a blockchain cannot be altered. Without the approval of the majority of network users, it is very difficult to change or reverse a transaction once it has been verified and published to the blockchain.
- Security: It’s cryptographic methods guarantee that data is private, safe, and impervious to unwanted modifications.
Together, these characteristics offer a high degree of accountability and confidence, particularly in settings where conventional institutions or middlemen would not be trusted.
Also Read: https://apkbeast.website/mastering-digital-marketing-dominate-online-world/
Redefining Trust in the Digital Age
In the past, trust has been built through middlemen that serve as authority to verify and authenticate transactions, such banks, governments, or businesses. Despite being effective for millennia, this paradigm has drawbacks. Data breaches, fraud, inefficiencies, and corruption are all possible with centralized systems. These middlemen also frequently charge exorbitant prices for their services, which leads to extra inefficiencies and friction.
By offering an alternate method of establishing confidence without the need for middlemen, blockchain disrupts this conventional paradigm. Instead of depending on a third-party authority, it allows parties to trust the system itself using cryptographic methods and consensus procedures. This is especially crucial in a time when consumers want more autonomy over their financial transactions and personal information and are growing more dubious of centralized organizations.
It, for instance, makes it possible for people to transfer and receive money without a bank or other financial entity handling the transaction. By guaranteeing that transactions are safe and final, the system lowers the possibility of fraud or disagreements. Blockchain can potentially reduce transaction costs by doing away with middlemen, increasing marginalized communities’ access to financial services.
Increasing Transparency with Blockchain
Another important advantage of blockchain technology is transparency. In a typical system, only specific parties have access to the data and transactions, which are frequently managed by centralized organizations. Corruption, inefficiencies, and a lack of responsibility can result from this lack of openness.
By enabling all network users to view and validate the same data, it, on the other hand, provides total transparency. On the blockchain, every transaction is tracked and its origin can be determined. Because every action is visible to everyone in the network and any attempt to change or tamper with the data would require the consent of the majority of participants, this fosters a high level of responsibility.
Supply chain management is one of the most effective uses of blockchain’s transparency. Blockchain technology allows businesses to follow the flow of commodities from point of origin to point of destination while guaranteeing fast, accurate, and verifiable information. By following a product’s path through the supply chain, consumers may confirm the legitimacy of luxury goods or organic food. In addition to increasing customer trust, this degree of openness aids companies in finding inefficiencies, lowering fraud, and streamlining operational procedures.
The Impact of Blockchain Across Industries
The potential of blockchain technology to redefine transparency and trust has broad ramifications for numerous industries. Here, we examine a few of the major industries that blockchain technology is revolutionizing.
Financial Services
One of the first industries to adopt blockchain technology was the financial sector. Cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum and Bitcoin have shown how blockchain technology may support decentralized financial systems. Due of its potential to offer quicker, less expensive, and more secure payment methods, traditional financial institutions are investigating blockchain technology.
Cross-border payments, which are usually costly and delayed because of middlemen and legal barriers, can be greatly shortened by using blockchain technology. Bypassing conventional banking institutions, blockchain-powered payment solutions allow for almost immediate, inexpensive transactions between parties in various nations.
It also has the ability to make financial services more accessible to anyone. Blockchain can offer banking services to the unbanked by doing away with the need for middlemen, particularly in developing nations where access to conventional banking infrastructure is limited.
Healthcare
Transparency, security, and data privacy are major issues for the healthcare sector. Interoperability between healthcare providers is lacking, and patient records are frequently dispersed across several systems. By offering a safe, unchangeable, and transparent method of storing and exchanging health data, blockchain can help with these problems.
Patients can keep custody of their medical records using blockchain technology, and they can authorize healthcare practitioners to access them as needed. In addition to providing healthcare providers with accurate and current information to use when making treatment decisions, this guarantees that sensitive health information is kept safe.
Furthermore, it can enhance the pharmaceutical supply chain by guaranteeing that medications are not counterfeit and are obtained from authorized producers. This is especially crucial in areas where the problem of fake medications is severe.
Supply Chain and Logistics
Another area where blockchain is having a big impact is supply chain management. This technology can offer complete insight into the flow of goods, guaranteeing that each stage of the supply chain is monitored and validated. This helps firms optimize their operations and lowers the chance of fraud, theft, and mistakes.
Retailers may use blockchain, for instance, to track the origin of goods like food and make sure they are obtained environmentally and ethically. Additionally, blockchain can simplify payments, lessen the administrative load related to supply chain documentation, and enhance inventory management.
Governance and Voting Systems
It is a viable instrument for improving democratic governance and electoral processes because of its transparency and immutability. Conventional voting methods are frequently susceptible to manipulation, fraud, and tampering. Elections may be held in a safe, transparent, and auditable manner with this technology, guaranteeing that each vote is counted precisely and cannot be changed after it has been submitted.
Furthermore, decentralized and transparent governance models that promote greater public confidence can be made possible by blockchain-based governance systems, which can provide citizens more direct authority over decision-making procedures.
Intellectual Property and Copyright
Patents, copyrights, and trademarks are examples of intellectual property (IP) rights that are frequently challenging to administer and uphold. By offering a decentralized ledger that documents ownership and license details, blockchain can assist in proving and enforcing intellectual property rights.
This technology can be used to track and manage the work of musicians, artists, and content producers, guaranteeing that they receive fair compensation for their contributions. Automating royalty payments and other IP-related transactions is possible using smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements constructed on blockchain.
Challenges and Opportunities
This technology has drawbacks even with its revolutionary promise. Among the main challenges are:
- Scalability: This networks may become less effective and slower as they expand. To increase blockchain scalability, innovations like sharding and layer-2 solutions are being investigated.
- Regulation: Businesses and investors are experiencing anxiety due to the absence of clear rules surrounding blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. Frameworks addressing topics including consumer protection, anti-money laundering, and data privacy are being developed by governments and regulators.
- Adoption: While it has the potential to revolutionize many industries, widespread adoption is still in its early stages. To successfully deploy blockchain technology, businesses must get beyond organizational, financial, and technical obstacles.
It offers enormous prospects in spite of these obstacles. We may anticipate that more industries will embrace blockchain as the technology develops and gains acceptance because of its potential to improve security, transparency, and trust.
Conclusion
In the digital age, trust and transparency are being redefined by the blockchain revolution. It is revolutionizing our interactions, transactions, and governance by offering a decentralized, transparent, and secure method of recording transactions. It has an immense potential to change the global economy and has an impact on a variety of industries, including finance, healthcare, supply chain, and governance.
Businesses, governments, and individuals must all embrace the benefits presented by this technology and collaborate to address its obstacles as we go forward. With trust built into the technology itself rather than relying on centralized authorities, blockchain offers the potential to build a more transparent, safe, and egalitarian world.